Algorithm
Gopl Exercise 5.2
输入为 HTML 源码,要求用一个 map 记录其中每个 element name (e.g. p, div, span…) 出现的次数。
https://github.com/JuneYuan/gopl.io/tree/master/ch5/ex_5_2
Review
Elasticsearch from the Bottom Up, Part 1
这篇文章介绍单个 ES 节点是怎么处理数据写入、内容搜索的。后续还有一篇 Top Down 的文章,介绍 ES 分布式方面的问题。
这一篇 Bottom Up, 从最基本的 Inverted Index 切入(文章形容它是个 “versatile data structure” =_=),阐明 ES 执行搜索的核心思想,就是把各种搜索问题都转化为 string prefix 类问题。给了一连串的例子,所以比较好理解。
接下来介绍 ES 中数据写入的特点。总的来说,在 search speed, index compactness, indexing speed, 和 sla of visibility 这几个指标中,ES 更侧重前两个,而搜索更快、index size 更小,都以牺牲 indexing speed 为代价。因此 ES 的数据写入有别于其他常见的数据库:delete 操作其实是在一个 bitmap 上打标记,并非立刻执行删除;而 update 则是通过一个 delete + 一个 insert 实现的,并非真正的“更新”。(“no in-place update of values”)
后边还介绍了ES 的数据组织方式,画出来大致是这样:
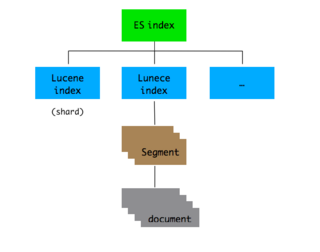
一个 document 写入 ES 时,首先要路由到某个 shard, 然后是 segment; 搜索则是先在每个 segment 上执行,然后合并结果。
看完这篇文章,就能够理解 ES 中的基本概念了。也可见作者的功底,篇幅不长,却能把关键问题说得很清楚。ES 官方文档给我的感觉也是这样,简短,易懂,是文档中读起来比较轻松的了。另外,文中有不少外部链接,没顾得上细看,等以后遇到问题再回头来查阅。
Excerpt
- The inverted index maps terms to documents (and possibly positions in the documents) containing the term.
一句话解释什么是 Inverted Index.
- the approach is the same: first, operate on the dictionary to find candidate terms, then on the corresponding occurrences, positions, etc.
一句话解释“搜索”是怎么做的。
- With an inverted index, we transform problems until they look like string-prefix problems.
…- An index term is the unit of search. The terms we generate dictate what types of search we can (and cannot) efficiently do.
…
In terms of complexity, looking up terms by their prefix is O(log(n)), while finding terms by an arbitrary substring is O(n).
为什么要把各种问题都转化为字符串前缀匹配问题:数据结构决定了它最擅长处理这类问题(复杂度低)。
- A “shard” is the basic scaling unit for Elasticsearch.
- … a shard is actually a complete Lucene index.
Tip
To Be Done.